AI algorithm helps Somerset clinicians detect lung cancer faster
- 18 August 2022
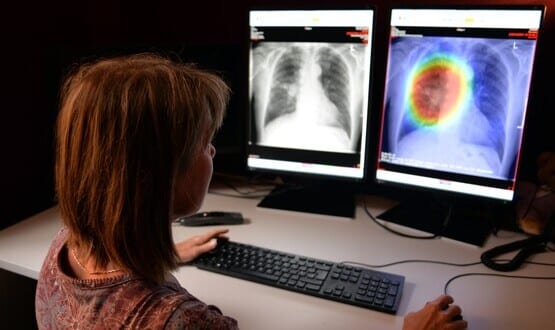
Somerset NHS Foundation Trust is piloting the use of an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm to detect lung cancer from x-rays faster.
The trust’s radiology team has been testing the clinical analysis software algorithm, called Behold.AI red dot, to find out if it could help in reducing the time it takes to diagnose patients for lung cancer.
Early results show that the software has played a part in helping the clinicians at Somerset to more than halve the time from the initial X-ray screening to a CT scan.
Dr Paul Burn, a consultant radiologist at Somerset, said: “There has been a lot of buzz about AI at our radiology meetings, but so far there has been little experience of using it in an NHS trust.
“By prioritising which x-rays need urgent attention from a radiologist, AI helped us to reduce the average time from chest x-ray to CT scan from 7 to 2.8 days, helping to complete the diagnostic cancer pathway within the national standard of 28 days. The reduction in time was due to a combination of both AI and speeding up our CT bookings.”
The red dot algorithm, developed in collaboration with NHS consultant radiologists, provides a subset of abnormal x-rays with a high probability of lung cancer, and another subset of x-rays (high confidence normal) with a very high likelihood of being normal.
Of the 3,794 chest x-rays reviewed by the algorithm over a period of three months, the average time for a result to enter the hospital systems was 16 seconds. The red dot service also classified 562 (14.8%) as high confidence normal (HCN).
“HCN results are an obvious opportunity for where AI can be used in the future. This could be particularly important for NHS trusts that see a high number of patients or experience longer than usual waits due to factors such as the Covid-19 pandemic,” Dr Burn added.
In 13 cases, radiologists disagreed with the model’s classification as HCN, giving a negative predictive value (NPV) of 97.7%, however none of these discrepancies were considered clinically significant.
Dr Michael Marsh, South West medical director for NHS England and NHS Improvement, said: “The pioneering work carried out by the radiology team at Somerset NHS Foundation Trust to test the AI technology in a hospital setting is a great example of innovation taking place in the South West NHS to reduce waiting times and improve outcomes for patients.”
Work is also taking place with AI to help detect lung cancer at Portsmouth Hospitals University NHS Trust, using the Sectra Amplifier Service set up by Sectra.
Through the service’s AI marketplace, Portsmouth Hospitals is assessing a deep learning algorithm that works on chest x-rays to identify abnormalities that may otherwise have been hidden by rib bone structures.



